Setting the Application Schema Path
What is the application schema?
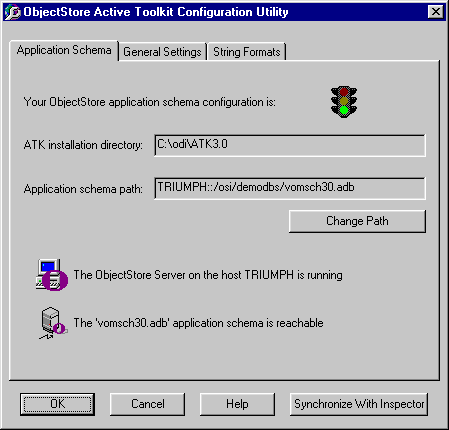
The application schema is an ObjectStore database in the file vomsch30.adb. In order for the application to access the application schema, the schema must be under the control of an ObjectStore Server. If you manually move the application schema, you must reconfigure ATK with the schema's new location.For example, suppose an application running on a Windows NT workstation that has no ObjectStore Server queries a Solaris ObjectStore Server. To successfully query the Solaris Server database, you must copy the application schema to the Solaris machine and reconfigure ATK on the Windows NT machine with the remote location of the Solaris workstation.
Default location
By default, the vomsch60.adb is placed in C:\odi\ATK6.0\lib. Use the Application Schema sheet to check or modify the ATK application schema path, and to configure ATK to use a particular ObjectStore Server located on your network.
Application Schema Sheet
The Application Schema sheet displays the ATK application schema configuration: