ObjectStore Active Toolkit Reference
Chapter 1
ATK and the Inspector
Introduction
ATK uses the data views and instance formats that you define in Inspector and store in the metaknowledge.
In this chapter
This chapter presents the following topics:
ATK Metaknowledge and Inspector
What is metaknowledge?
Inspector metaknowledge contains data view definitions, including the query and ordering information set by the query's author, and other information about the database schema and the defined instance formats.
ATK provides read and write access, by means of the ATK ActiveX server or the ATK OLE DB provider, to data views you define in the Inspector. To do this, ATK must process the ObjectStore database's metaknowledge, which Inspector stores.
ATK's use of metaknowledge
Inspector uses the metaknowledge to display persistent instances, and ATK uses the Inspector metaknowledge to retrieve information about the available data views, instance formats, and schema structure. Thus, the Inspector metaknowledge logically becomes the ATK metaknowledge. Although ATK never modifies this metaknowledge, by using ATK you can customize the data view and instance format definitions and reuse Inspector-defined data views in different contexts.
Metaknowledge location
Inspector metaknowledge can reside in the file system, in the same inspected database, or in another ObjectStore database that contains only Inspector metaknowledge. The metaknowledge location is specified in the Inspector configuration.
ATK must be able to access the Inspector metaknowledge. When you install ATK, the installation program verifies that the Inspector is installed, examines the Inspector configuration to determine where the metaknowledge resides, and configures ATK with that location. Thus, ATK can access the data views and instance formats you define using Inspector.
To modify the ATK configuration, refer to Chapter 4, Configuring ATK.
Accessing Data Views and Instance Formats from ATK
What is a data view?
A data view is a tabular representation of a persistent ObjectStore collection that uses a specified instance format to display persistent instances. You can define a data view based on any of the following:
· Filtering options
· Ordering options
· Arrays
· User-defined extent methods
For example, suppose the class Customer has two data members, name and address. You can use Inspector to build a data view based on a collection of customers. A data view's instance format specifies the set of data members that must be displayed for an instance of the class in the data view. If you are displaying a table of instances, the instance format specifies what columns have to be displayed. This simple data view has an instance format of two columns that represent the name and address of each Customer object contained in the persistent collection.
Defining a filter to list only those customers whose names start with the letter J, or defining an order that lists the customers alphabetically, makes this data view more complex.
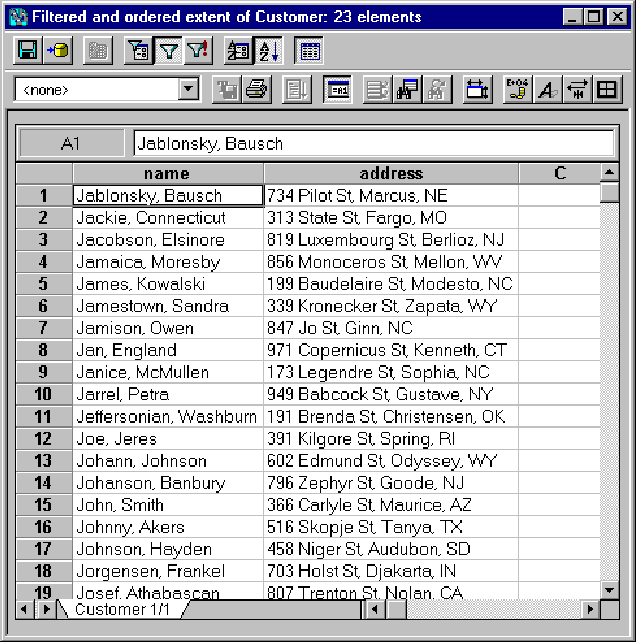
You can name and save the view, and reload it later. If the collection changes, the data view changes accordingly.
Accessing Data Views from ATK
To access a data view defined in Inspector, use the ATK ActiveX server or ATK OLE DB provider and specify the name of the data view.
For example, to access a data view named my_first_dataview through the ATK ActiveX server, create an IATKDataView object to represent the view:
atkDataView = atkDatabase.GetDataView("my_first_dataview")
Using the ATK OLE DB provider, open a record set representing the same data view:
adoRecordSet.Open("my_first_dataview", adoConnection)
You can also use SQL statements with OLE DB:
adoRecordSet.Open("SELECT * FROM my_first_dataview",
adoConnection)
Note that if you use SQL statements, the data view name must follow SQL syntax rules.
Accessing Instance Formats from the ATK ActiveX Server
Using the ATK ActiveX server, you can directly access the instance formats defined for the classes contained in the database schema. An instance format can include navigation pointers and collections of other classes, which provide a powerful means of navigating among objects transparently and displaying the equivalent of relational SQL joins faster and more efficiently than SQL syntax.
When you create a data view in Inspector, you can save the data view template with a symbolic name. When you modify an instance format in Inspector, you usually modify the default instance formats associated with each class. However, the Inspector will save any modification to the template instance format using the symbolic name. The ATK ActiveX server accesses this name and displays data according to the specified instance format.
Refer to Chapter 2, Accessing ATK ActiveX Server from ASP Applications, in the ObjectStore Active Toolkit Tutorial, for an example of defining multiple instance formats for a specific class and accessing them from the ATK ActiveX server, and customizing a data view using the ATK ActiveX server or ATK OLE DB provider.
[previous] [next]
Copyright © 1998 Object Design, Inc. All rights
reserved.
Updated: 05/11/99 11:33:45

